Overview
A method of diffusion bonding of a lead zirconate-titanate (PZT) piezoelectric crystal to a metal wear plate for fabrication of a high temperature ultrasonic transducer was developed. Bringing the bonding surfaces of the noble metal coated PZT crystal and the bonding surface of the noble metal coated metal wear plate into contact with each other and heating under pressure at a temperature of 250°C to form a metallic bond to obtain a lead zirconate-titanate (PZT) piezoelectric crystal diffusion-bonded to the metal wear plate by the noble metal interlayer under vacuum; wherein, the metal interlayer is able to withstand a prolonged exposure to high temperature up to 250°C and repeated thermal cycling.
Photograph of bonded transducer element

Quick View Leaflet
A method of diffusion bonding of a lead zirconate-titanate (PZT) piezoelectric crystal to a metal wear plate for fabrication of a high temperature ultrasonic transducer was developed. Bringing the bonding surfaces of the noble metal coated PZT crystal and the bonding surface of the noble metal coated metal wear plate into contact with each other and heating under pressure at a temperature of 250°C to form a metallic bond to obtain a lead zirconate-titanate (PZT) piezoelectric crystal diffusion-bonded to the metal wear plate by the noble metal interlayer under vacuum; wherein, the metal interlayer is able to withstand a prolonged exposure to high temperature up to 250°C and repeated thermal cycling.
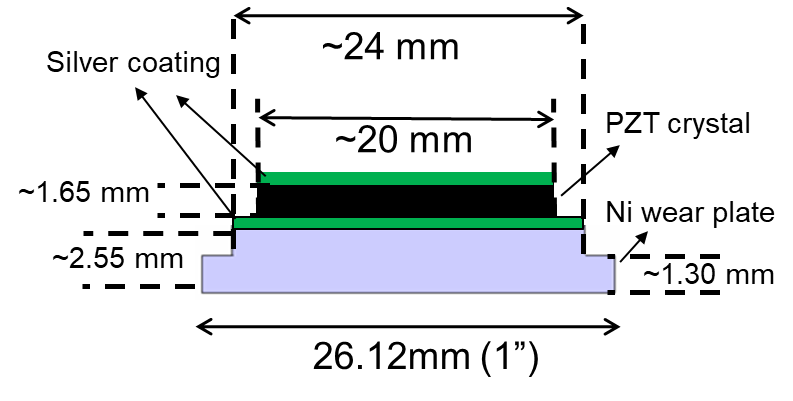
Specifications of PZT crystal and Ni-wear plate:
Below is the schematic of bonded crystal. It includes a) 1 MHz PZT crystal (1.65 mm thick and 20 mm diameter), b) Step machined Nickel-wear plate (2.55 mm thick with 1.30 mm step).
Schematic of diffusion bonded PZT transducer with Ni-base
Detailed Technical Brochure
Technical Specifications
Under Sodium Ultrasonic scanner (USUSS) has been developed to view the internal components of Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors (SFRs). In-house developed high temperature ultrasonic transducers (UT) capable of working in sodium at 180°C are used in the USUSS. In these transducers, solder alloy (96.5% Sn - 3.5% Ag) having a melting point of 220°C is used to bond the Lead zirconatetitanate (PZT) crystal with the nickel base. The temperature of primary sodium during the reactor shutdown in SFR would be around 250°C. Hence, sodium temperature needs to be further reduced and brought down to 180°C before deploying the scanner. Considering the difficulties in bringing down the temperature of sodium to 180°C, it has become necessary to develop transducers which can work in sodium at 250°C. Hence, the bonding of the piezoelectric ceramic to nickel in USUSS needs to withstand continuous operation at 250°C. This report describes the different stages of development of the bonding process to meet these requirements.

PROCESS
• Rinse the PZT crystals and Ni-base with IPA and acetone.• Deposit about 1µm fresh silveron the existing ~30µm silver layer of PZT crystal by DC magnetron sputtering.
• Deposit the Ni-base with ~2µm silver by DC magnetron sputtering and heat under the hydrogen atmosphere at 800°C for 1h. Repeat the coating and heating under the hydrogen atmosphere second time.
• Deposit the Ni-base finally with ~ 3µm silver by DC magnetron sputtering.
• Place the silver-deposited surfaces of PZT and Ni-base facing each other in the specially designed holder of the bonding facility.
• Evacuate the vessel using rough vacuum pump.
• By uniaxial press, lower the plunger to a pressure of 200 bar and start heating the furnace at 5K min-1 to 250°C.
• Heat the system for about one hour and cool under evacuation.
• Stop evacuation and release the pressure.
• Take the bonded sample from the vessel for further characterization and use.
SALIENT FEATURE
• Quality of bonding was certified with C-scan imaging technique• Ready to configure with transducer housing
• Maximum temperature of operation: 250°C
ADVANTAGES
• Suitable for viewing in opaque fluid media like liquid sodium• Configured for high temperature (250°C) usage
AREAS OF APPLICATION
• Nuclear installationsFACILITIES REQUIRED
• Heating, deposition and bonding facilities could be installed in a 15 x 10 feet room.• DC magnetron sputtering unit, High vacuum pumping system, uni-axial pressing unit, Split furnace, Inconel vessel and specially designed SS vessel with pellet guiding accessory for bonding.
Application Procedure for Transfer of Technology from IGCAR
Who can apply
Interested parties with Engineering & Scientific knowledge, good financial background and adequate experience of products manufacturing & fabrication with technical capability in the area of interested technology and having or interested in setting –up facilities for production would be preferred.
How to apply
Send your Technology Transfer Application form duly filled and signed along with a Demand Draft/Bankers cheque of Rs. 500/- (for Indian entities) or US $50/- (for foreign entities) drawn in favour of “Accounts Officer, IGCAR” as application processing fee on following address:
Head, Incubation Centre- IGCAR,
Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research,
Kalpakkam, 603 102, India.
Note:Applications without processing fee as applicable above of Rs. 500/- or US $50/- for each technology will not be considered.
Click here for Technology Transfer Application Form